Ⅰ. Product introduction
PRECI SCS-R300 is a collection of confocal Raman spectroscopy detection system with single cell visual separation system for the integration of cell recognition and separation equipment, based on Raman spectroscopy identification of target bacteria, and sequencing on the single cell level, culture and other research, building the bridge unicellular phenotype and genotype, It provides a new strategy for single cell research in various fields. In addition, Raman separation technology can also be used for the identification and separation of microplastics and other small particles.
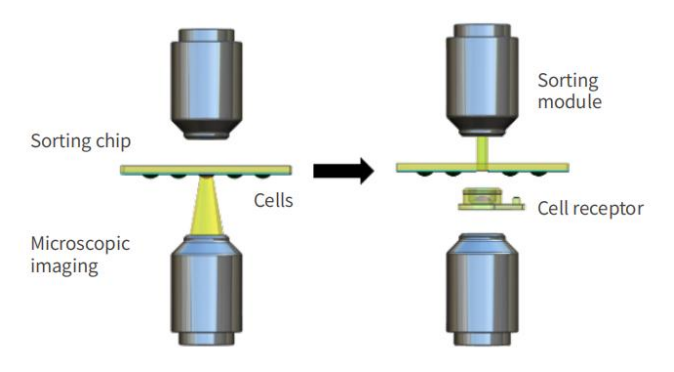
Principle of PRECI SCS-R300 single cell sorter
Ⅱ、Significance of microbial single cell research
Single cell research is a hot research field in biology. However, the research on microbial single cells is still in its infancy, so the realization of microbial single cell identification, rapid screening of functional bacteria, microbial identification, visual single cell isolation and high-throughput screening will provide technical breakthroughs for microbial research.
Traditional population research methods: the average value can not reflect the function of different cells in the community. Macrogene sequencing can reflect the composition and abundance of a community, but it still cannot pinpoint which microorganism plays a key role.
New technology for single-cell research: It can bypass the culture stage, establish the association between phenotype and genotype at the single-cell level, effectively solve the problems existing in population research, and provide new strategies for the study of functional microorganisms, mutant strains, drug-resistant bacteria, and unculture-resistant microorganisms.
Ⅲ、Microbial single cell research strategies
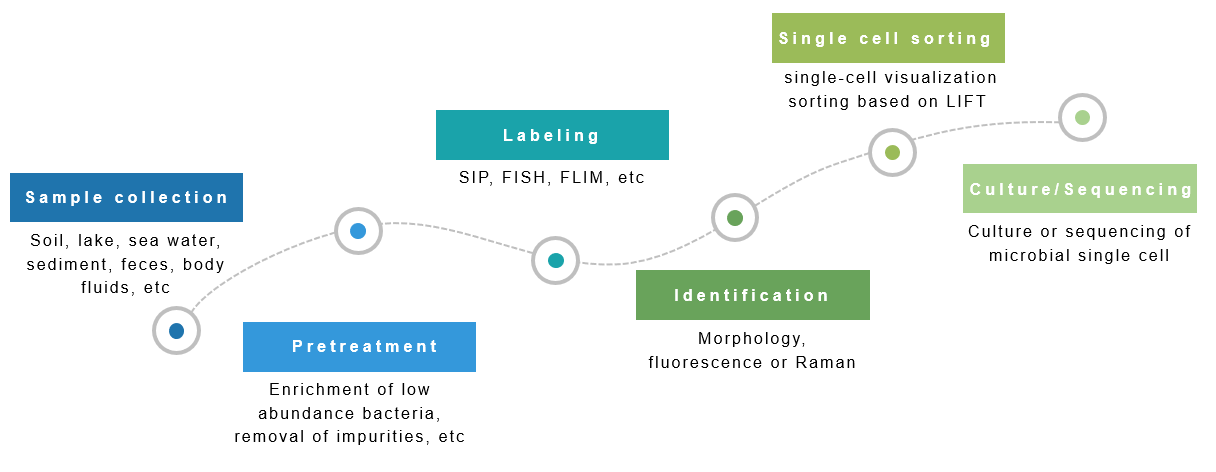
Ⅳ、The research field
Cell biology (cell types identification, cell metabolism, etc.), plant developmental biology, genetics and breeding, genetic mechanism, etc.), genetics (stem cell growth, differentiation and mature dynamic monitoring, etc.), microbiology, microbial species identification and drug susceptibility testing, etc.), pathology (tumor precise separation, intraoperative navigation, fast pathologic analysis, etc.), pharmacokinetic (drugs Metabolic monitoring in cells, etc.), immunology (immune microenvironment, etc.), food science (food safety, fermentation engineering bacteria, etc.), etc.
Ⅴ、The experimental scheme
1. Single cell isolation of microorganisms based on morphology
According to the length, width, aspect ratio, regularity and other morphological indicators of the microbial cells, the identification, positioning and numbering are carried out, and the single cells of the target morphology are automatically separated.
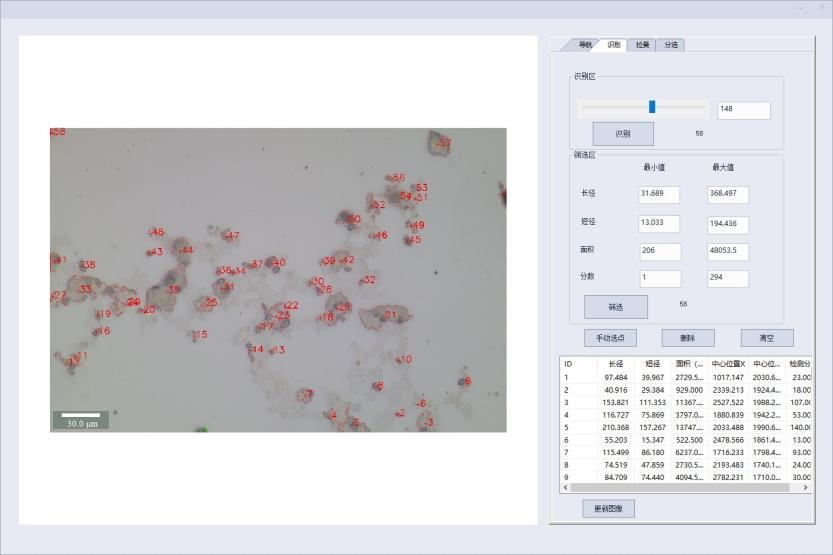
Microbial single cell intelligent image recognition function
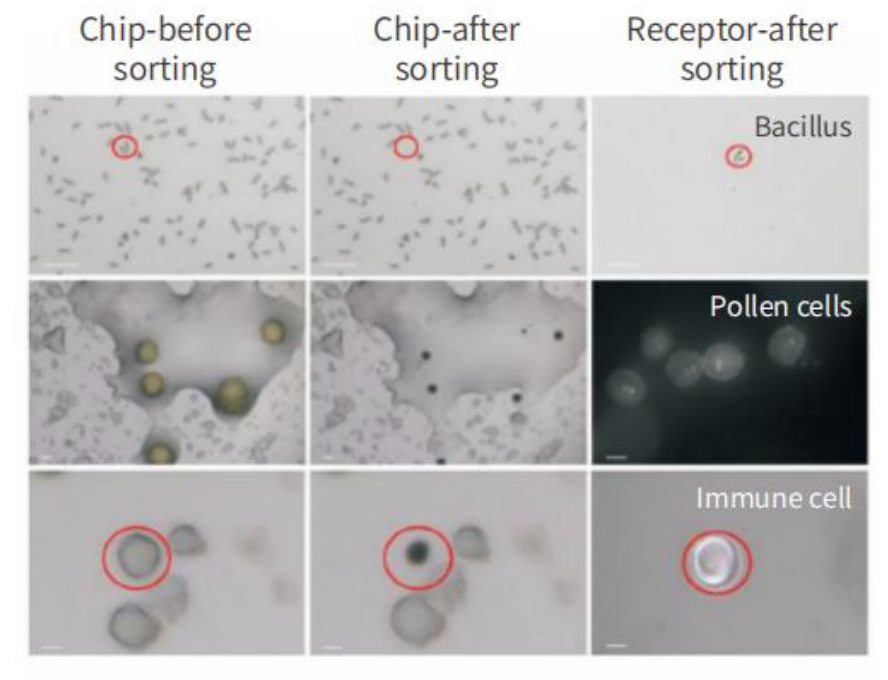
Single cell sorting results
2. Raman identification of drug-resistant bacteria / functional microorganisms (e.g. organic-degrading bacteria)
Heavy water labeling: for metabolically active microbial cells, D2O will enter the carbon skeleton through metabolism, form C-D bond, and make the peak position red shift to the silent zone. Using this method, the metabolic activity of bacteria/cells under stressful conditions (e.g., antibiotics, high temperature, high pressure, etc.) can be detected to identify drug-resistant bacteria or extremophiles.
13C and 15N stable isotope labeling: 13C and 15N isotope probes to the substrate complete tag for biomarkers, with a heavy isotope of biomarkers, the characteristics of Raman spectral lines with an effect will occur red mobile (isotope rate > 10%), using spectral analysis easily identified, and single target microorganisms.
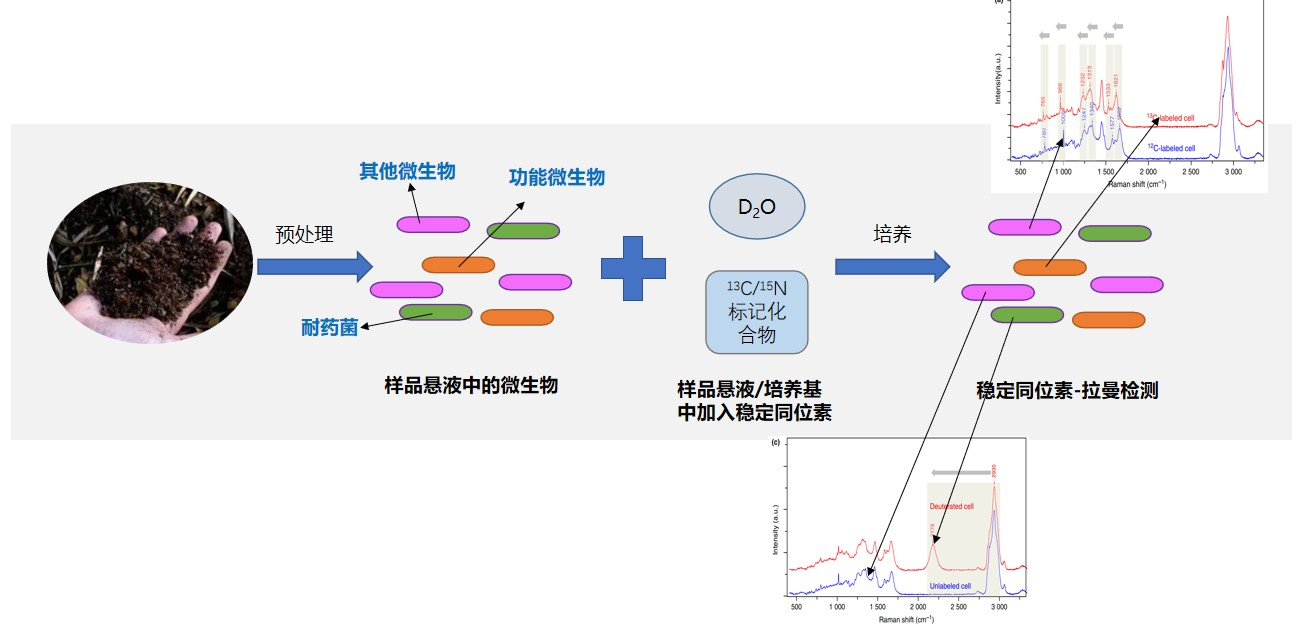
Raman identification process of functional bacteria
Ⅵ、The applications

1. Study on intestinal drug-resistant microorganisms
In this paper, a combination of isotope-Raman spectroscopy, single cell sorting and mini-Meta sequencing analysis was used to study the drug-resistant microbiota in human intestinal microbiota, and to reveal the correlation between intestinal drug-resistant bacteria and individual drug history.
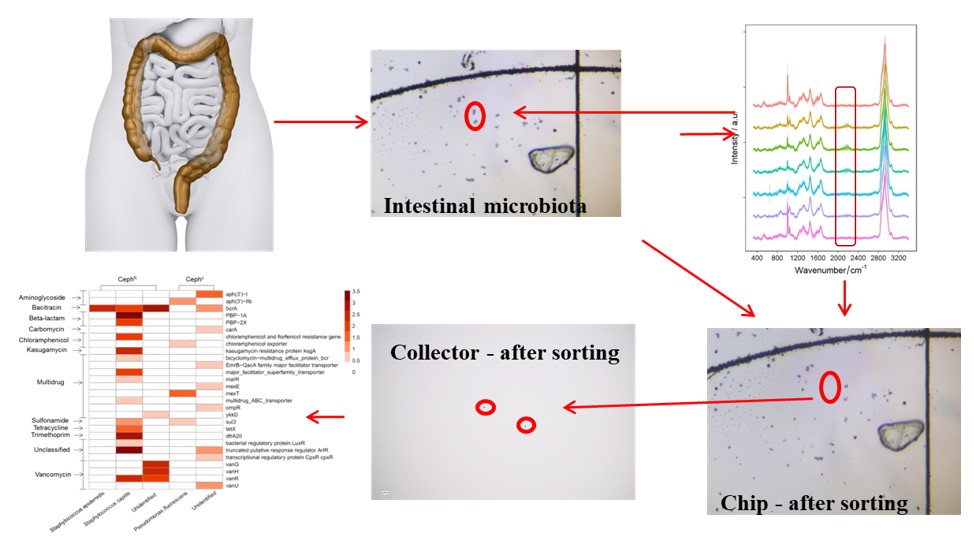
Raman-activated sorting of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in human gut microbiota
2. D2O probe traced the horizontal transfer of drug resistance genes
Single-cell Raman spectroscopy combined with reverse D2O labeling (Raman-rD2O) is a sensitive and rapid phenotypic tool that can be used to track the spread of plasmids carrying antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) from soil to clinical bacteria through transformation. Raman-rD2O sensitively identifies low abundance phenotypic resistant transformants from a large number of recipient cells, and then combines single cell sorting to obtain target transformants and perform gene identification to explore horizontal transfer of drug resistance genes.
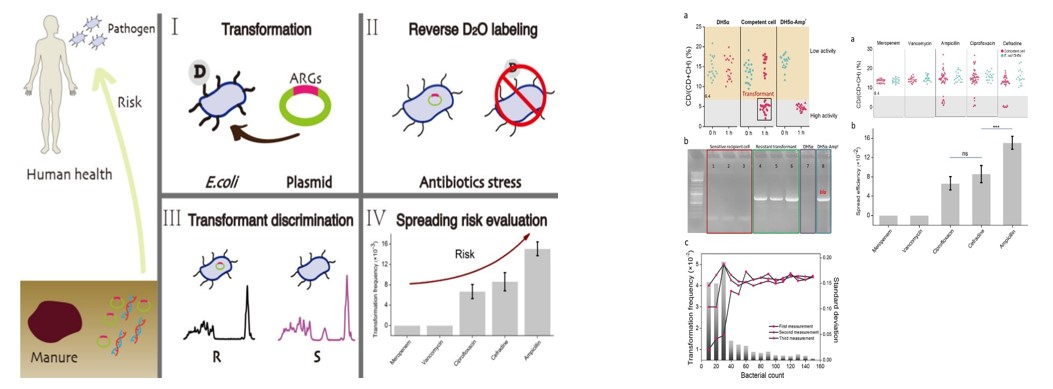
Phenotypic Tracking of Antibiotic Resistance Spread via Transformation for Environment to Clinic
3. Single cell isolation of microorganisms based on fluorescence
Single cells were identified and isolated based on the fluorescence signals of the target bacteria (autofluorescence, fluorescent dyes, probe labeling, FISH, etc.).
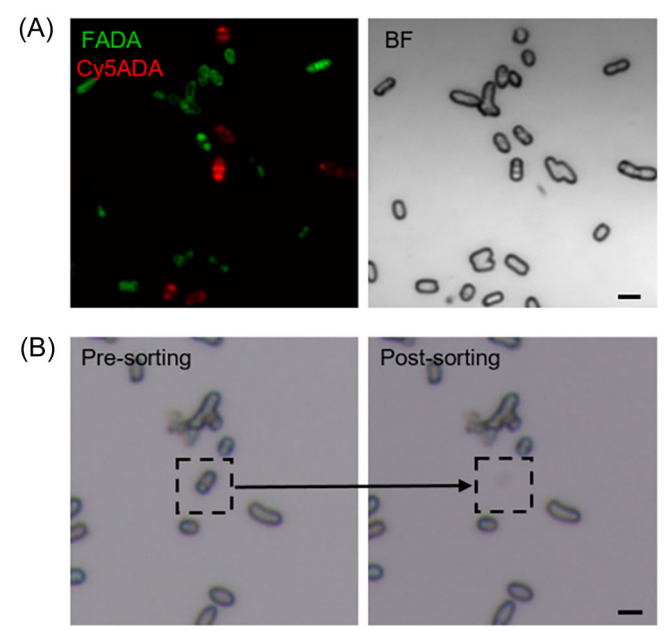
Integrated identification of growth pattern and taxon of bacterium in gut microbiota via confocal fluorescence imaging‐oriented single‐cell sequencing